|
|
|
The polygamma function is sometimes denoted ![]() , and sometimes
, and sometimes ![]() . In
. In ![]() notation,
notation,
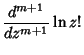 |
(1) | ||
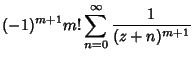 |
(2) | ||
| (3) |
![$\displaystyle {d^{m+1}\over dz^{m+1}} \ln[\Gamma(z)]$](p2_1227.gif) |
|||
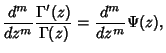 |
(4) |
| (5) |
The polygamma function obeys the Recurrence Relation
| (6) |
| (7) |
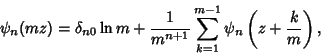 |
(8) |
In general, special values for integral indices are given by
| (9) | |||
| (10) |
| (11) | |||
| (12) | |||
| (13) | |||
| (14) |
R. Manzoni has shown that the polygamma function can be expressed in terms of Clausen Functions
for Rational arguments and integer index. Special cases are given by
| (15) | |||
| (16) | |||
| (17) | |||
| (18) | |||
| (19) | |||
![$\displaystyle -{4\pi^3\over 3\sqrt{3}}-18\mathop{\it Cl}\nolimits _3(0)+9[\math...
...extstyle{2\over 3}}\pi)+\mathop{\it Cl}\nolimits _3({\textstyle{4\over 3}}\pi)]$](p2_1260.gif) |
|||
| (20) | |||
![$\displaystyle {4\pi^3\over 3\sqrt{3}}-18\mathop{\it Cl}\nolimits _3(0)+9[\matho...
...extstyle{2\over 3}}\pi)+\mathop{\it Cl}\nolimits _3({\textstyle{4\over 3}}\pi)]$](p2_1262.gif) |
|||
| (21) | |||
| (22) | |||
| (23) | |||
| (24) | |||
| (25) | |||
| (26) | |||
| (27) |
See also Clausen Function, Digamma Function, Gamma Function, Stirling's Series
References
Abramowitz, M. and Stegun, C. A. (Eds.). ``Polygamma Functions.'' §6.4 in
Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables, 9th printing.
New York: Dover, p. 260, 1972.
Adamchik, V. S. ``Polygamma Functions of Negative Order.'' Submitted to
J. Symb. Comput.
Arfken, G. ``Digamma and Polygamma Functions.'' §10.2 in Mathematical Methods for Physicists, 3rd ed.
Orlando, FL: Academic Press, pp. 549-555, 1985.
Davis, H. T. Tables of the Higher Mathematical Functions. Bloomington, IN: Principia Press, 1933.
Kolbig, V. ``The Polygamma Function
Morse, P. M. and Feshbach, H. Methods of Theoretical Physics, Part I. New York: McGraw-Hill, pp. 422-424, 1953.
![]() for
for ![]() and
and ![]() .'' J. Comp. Appl. Math. 75, 43-46, 1996.
.'' J. Comp. Appl. Math. 75, 43-46, 1996.
|
|
|
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein